Unveiling the Human Skin Color Evidence for Selection Answer Key: An Evolutionary Perspective delves into the intriguing interplay between natural selection and human skin color diversity. This comprehensive exploration unravels the captivating narrative of how environmental pressures have shaped our skin tones over millennia.
Delving into the realm of evolutionary biology, this discourse examines the compelling evidence supporting the role of natural selection in sculpting human skin color. Geographic distribution patterns, genetic studies, and the correlation between skin color and UV radiation exposure paint a vivid picture of the selective forces that have influenced our skin’s pigmentation.
Introduction

Human skin color is a fascinating and complex evolutionary trait that has been shaped by natural selection over thousands of years. Skin color plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature, protecting against harmful UV radiation, and providing camouflage. Understanding the evolution of skin color can provide insights into the diverse adaptations that have allowed humans to thrive in different environments.
Natural selection is the driving force behind the evolution of skin color. It occurs when individuals with certain traits are better adapted to their environment and have a higher chance of survival and reproduction. Over time, these advantageous traits become more common in the population.
Evidence for Selection
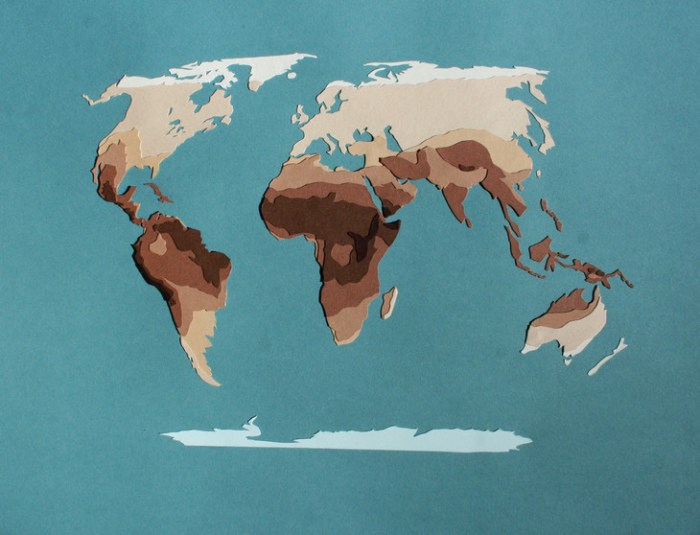
There is ample evidence to support the role of natural selection in shaping human skin color. One of the most compelling pieces of evidence is the geographic distribution of skin color variations. In general, people living closer to the equator have darker skin than those living in higher latitudes.
This pattern can be explained by the fact that darker skin provides protection against the harmful effects of UV radiation. In areas with high levels of UV radiation, darker skin is more effective at absorbing and scattering UV rays, reducing the risk of skin cancer and other skin damage.
Mechanisms of Selection, Human skin color evidence for selection answer key
Natural selection operates through a variety of mechanisms, including differential survival, differential reproduction, and sexual selection. Differential survival occurs when individuals with certain traits are more likely to survive and reach reproductive age. Differential reproduction occurs when individuals with certain traits are more likely to have offspring that survive and reproduce.
Sexual selection occurs when individuals with certain traits are more likely to attract mates and reproduce. In the case of skin color, sexual selection may have played a role in the evolution of lighter skin in some populations. Lighter skin is often associated with youthfulness and health, which may have been attractive to potential mates.
Essential Questionnaire: Human Skin Color Evidence For Selection Answer Key
What are the key mechanisms driving natural selection in skin color?
Natural selection favors traits that enhance survival and reproductive success in a given environment. In the case of skin color, lighter skin tones offer protection against UV radiation damage in regions with high sunlight exposure, while darker skin tones provide better protection against folate deficiency in areas with lower sunlight.
How does sexual selection influence skin color preferences?
Sexual selection can play a role in skin color preferences, as certain skin tones may be perceived as more attractive or desirable within specific cultural or social contexts. These preferences can influence mate selection and contribute to the distribution of skin color variations within populations.
What are the ethical and scientific controversies surrounding skin color research?
Skin color research has been subject to ethical and scientific controversies, particularly regarding the interpretation of data and the potential for misuse or misrepresentation. It is crucial to approach such research with sensitivity, acknowledge historical biases, and prioritize the responsible use of findings to promote understanding and reduce discrimination.