Introducing the Unit 3 Linear Relationships Answer Key PDF, an invaluable resource that empowers students to master the intricacies of linear functions. This guidebook serves as a beacon of clarity, providing a comprehensive understanding of the concepts, graphing techniques, equation writing, and real-world applications of linear relationships.
Embark on an educational journey where the complexities of linear functions unravel, revealing their significance in diverse fields.
Delving into the depths of linear relationships, we will explore the fundamental concepts that govern these functions, uncovering the secrets of their behavior. From understanding the different types of linear relationships to graphing them with precision, this guidebook unravels the mysteries of linear functions, transforming them from abstract ideas into tangible tools for problem-solving.
Unit 3 Linear Relationships: Unit 3 Linear Relationships Answer Key Pdf
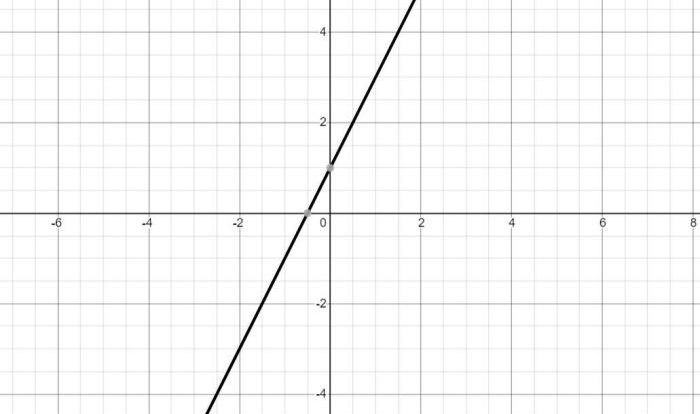
Linear relationships are mathematical equations that represent a straight line. They are characterized by a constant rate of change, which is known as the slope. Linear relationships can be used to model a wide variety of real-world phenomena, such as the relationship between the height of a child and their age.
Types of Linear Relationships, Unit 3 linear relationships answer key pdf
- Positive linear relationships: The slope is positive, indicating that as one variable increases, the other variable also increases.
- Negative linear relationships: The slope is negative, indicating that as one variable increases, the other variable decreases.
- Zero linear relationships: The slope is zero, indicating that there is no relationship between the two variables.
Graphing Linear Relationships
Linear relationships can be graphed on a coordinate plane. The slope of the line is determined by the ratio of the change in the y-coordinate to the change in the x-coordinate.
Parts of a Linear Graph
- x-intercept: The point where the line crosses the x-axis.
- y-intercept: The point where the line crosses the y-axis.
- Slope: The ratio of the change in the y-coordinate to the change in the x-coordinate.
Writing Linear Equations
Linear equations can be written in several different forms:
- Slope-intercept form: y = mx + b
- Point-slope form: y – y1 = m(x – x1)
- Standard form: Ax + By = C
Solving Linear Equations
Linear equations can be solved using a variety of methods:
- Substitution
- Elimination
- Graphing
Applications of Linear Relationships
Linear relationships have a wide variety of applications in real life, such as:
- Predicting the future value of an investment
- Determining the relationship between the speed of a car and the distance it travels
- Modeling the growth of a population
FAQ Compilation
What is the slope-intercept form of a linear equation?
The slope-intercept form of a linear equation is y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
How do you graph a linear equation?
To graph a linear equation, first find the y-intercept (the point where the line crosses the y-axis). Then, use the slope to find additional points on the line.
What is the difference between a positive and negative slope?
A positive slope indicates that the line is rising from left to right, while a negative slope indicates that the line is falling from left to right.