Analyzing graphics the carbon cycle – Analyzing Graphics: Unraveling the Carbon Cycle’s Secrets delves into the captivating realm of the carbon cycle, where intricate processes and profound implications intertwine. This comprehensive exploration unveils the essential components, intricate dynamics, and far-reaching significance of this fundamental Earth system.
Through meticulous analysis of graphical representations, we embark on a journey to decipher the language of the carbon cycle, unravel its mysteries, and illuminate its profound impact on our planet’s delicate balance.
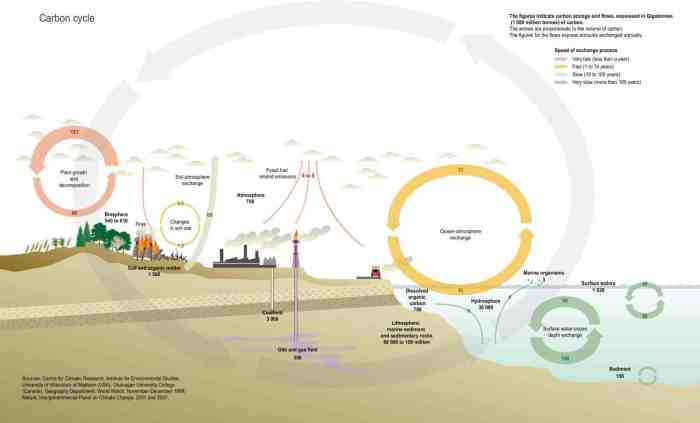
The Carbon Cycle: An Overview
The carbon cycle is a fundamental process that regulates the distribution and movement of carbon within the Earth’s systems. It involves the exchange of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms. The cycle plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of carbon in the atmosphere and influencing Earth’s climate.
The carbon cycle consists of several key processes, including photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and ocean-atmosphere exchange. Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and converts it into organic matter, while respiration releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Decomposition breaks down organic matter and releases carbon dioxide and methane, while ocean-atmosphere exchange allows carbon dioxide to dissolve into the oceans.
Importance of the Carbon Cycle, Analyzing graphics the carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is essential for life on Earth. It provides the carbon necessary for the formation of organic molecules, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. The cycle also regulates Earth’s climate by absorbing and releasing carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming.
Analyzing Graphics: Methods and Techniques

Graphics analysis is a valuable tool for understanding the carbon cycle. Various methods and techniques can be used to extract and visualize data from graphics related to the carbon cycle.
Data Extraction
- Manual extraction: Manually extracting data from graphics using tools like rulers, protractors, and calculators.
- Software extraction: Using software tools like ImageJ, GetData Graph Digitizer, or WebPlotDigitizer to extract data points.
Data Visualization
- Scatter plots: Used to visualize the relationship between two variables, such as carbon dioxide concentration and temperature.
- Line graphs: Used to show trends over time, such as the change in carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere.
- Bar charts: Used to compare different categories or groups, such as carbon emissions from different countries.
Data Cleaning and Validation
Data cleaning and validation are crucial to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the analysis. This involves removing outliers, correcting errors, and verifying the consistency of the data.
Key Metrics and Indicators
Several key metrics and indicators are used to measure and track the carbon cycle.
Carbon Dioxide Concentration
Carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is a primary indicator of the balance of the carbon cycle. It is measured in parts per million (ppm) and has been steadily increasing since the Industrial Revolution.
Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is a measure of the acidity of the oceans. As carbon dioxide dissolves into the oceans, it forms carbonic acid, which lowers the pH of the water. Ocean acidification can have negative impacts on marine life.
Carbon Sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the process of capturing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This can be done through natural processes, such as photosynthesis, or through technological methods, such as carbon capture and storage.
Data Visualization and Interpretation
Data visualization is essential for interpreting the results of graphics analysis. Tables, graphs, and charts can be used to present data in a clear and concise manner.
Tables
Tables are used to present numerical data in a structured format. They can be used to compare different categories or groups, such as carbon emissions from different countries.
Graphs and Charts
Graphs and charts are used to visualize trends and patterns in data. Scatter plots, line graphs, and bar charts are commonly used to display carbon cycle data.
Interpretation
Interpreting data visualizations requires an understanding of the context and the variables being measured. It is important to consider the scale of the data, the units of measurement, and any potential outliers or errors.
Case Studies and Applications: Analyzing Graphics The Carbon Cycle
Graphics analysis has been used in numerous case studies and applications related to the carbon cycle.
Case Study: Carbon Emissions from Fossil Fuels
Graphics analysis was used to analyze data on carbon emissions from fossil fuels. The results showed a strong correlation between the burning of fossil fuels and the increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration.
Application: Monitoring Carbon Sequestration
Graphics analysis is used to monitor the effectiveness of carbon sequestration projects. By tracking the change in carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere, researchers can assess the impact of these projects on the global carbon cycle.
Helpful Answers
What are the key components of the carbon cycle?
The carbon cycle involves the continuous exchange of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms.
How does analyzing graphics contribute to understanding the carbon cycle?
Graphical representations allow researchers to visualize trends, patterns, and relationships within carbon cycle data, facilitating deeper insights and informed decision-making.
What are some common metrics used to measure the carbon cycle?
Key metrics include atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration, ocean acidification, and terrestrial carbon storage, which provide valuable indicators of the cycle’s health and balance.