Select all true statements about lycophytes. – Select All True Statements About Lycophytes: Delving into the Realm of Lycophytes, an Ancient Lineage of Non-Flowering Plants.
Lycophytes, an enigmatic group of non-flowering plants, have captivated the scientific community for centuries. Their unique characteristics, diverse habitats, and ecological significance make them a fascinating subject of study. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the captivating world of lycophytes, unraveling their secrets and highlighting their importance in the tapestry of life.
Lycophyte Characteristics: Select All True Statements About Lycophytes.
Lycophytes are a group of non-flowering vascular plants that are characterized by their small size, simple leaves, and lack of true roots. They have a vascular system that consists of xylem and phloem, which allows them to transport water and nutrients throughout their bodies.
Lycophytes reproduce by spores, which are produced in sporangia. The spores are dispersed by the wind and can germinate to form new plants. Lycophytes have a life cycle that includes both a sporophyte and a gametophyte phase.
Lycophyte Classification
Lycophytes are classified into three main groups: club mosses, quillworts, and selaginellas.
Club Mosses
- Club mosses are the most common type of lycophyte.
- They have erect stems with small, scale-like leaves.
- Club mosses produce spores in cone-shaped sporangia.
Quillworts, Select all true statements about lycophytes.
- Quillworts are aquatic lycophytes that live in lakes and ponds.
- They have long, slender leaves that are arranged in a whorl.
- Quillworts produce spores in sporangia that are located at the base of their leaves.
Selaginellas
- Selaginellas are a group of lycophytes that have creeping stems.
- They have small, scale-like leaves that are arranged in four rows.
- Selaginellas produce spores in sporangia that are located in the axils of their leaves.
Lycophyte Habitats and Distribution
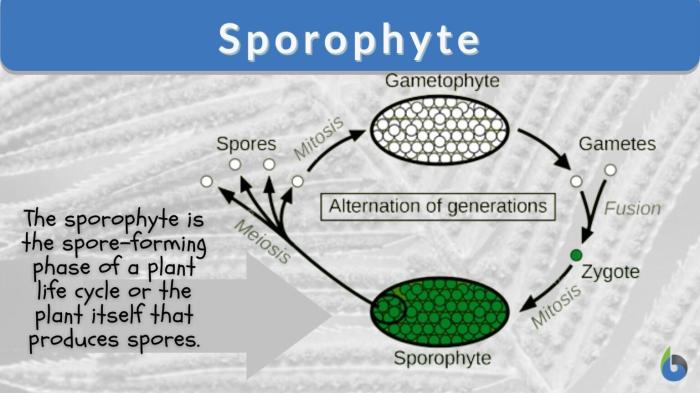
Lycophytes are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, wetlands, and deserts.
They are most common in humid environments, but some species can tolerate dry conditions.
Lycophytes are found on all continents except Antarctica.
Lycophyte Ecology and Importance
Lycophytes play an important role in the ecosystem.
They provide food and habitat for a variety of animals, including insects, amphibians, and reptiles.
Lycophytes also help to stabilize the soil and prevent erosion.
Lycophyte Adaptations
Lycophytes have developed a number of adaptations that help them to survive in their environment.
These adaptations include:
- Small size
- Simple leaves
- Lack of true roots
- Vascular system
- Spore production
- Ability to tolerate a wide range of environmental conditions
These adaptations have allowed lycophytes to survive for over 400 million years.
FAQ Insights
What are the key characteristics of lycophytes?
Lycophytes are characterized by their lack of flowers and seeds, their vascular structure, and their unique reproductive methods involving spores.
How do lycophytes reproduce?
Lycophytes reproduce through the production of spores, which are dispersed by wind or water and germinate to form new plants.
What are the different types of lycophytes?
Lycophytes are classified into three main groups: club mosses, quillworts, and selaginellas.