Cycles of matter worksheet answers provide an in-depth exploration of the fundamental processes that govern the movement of matter through the Earth’s systems. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the water, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur cycles, unraveling their significance for life on our planet.
Each cycle is meticulously examined, shedding light on the intricate interplay of physical, chemical, and biological processes that shape the Earth’s ecosystems. From the evaporation of water to the decomposition of organic matter, the cycles of matter play a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of our planet.
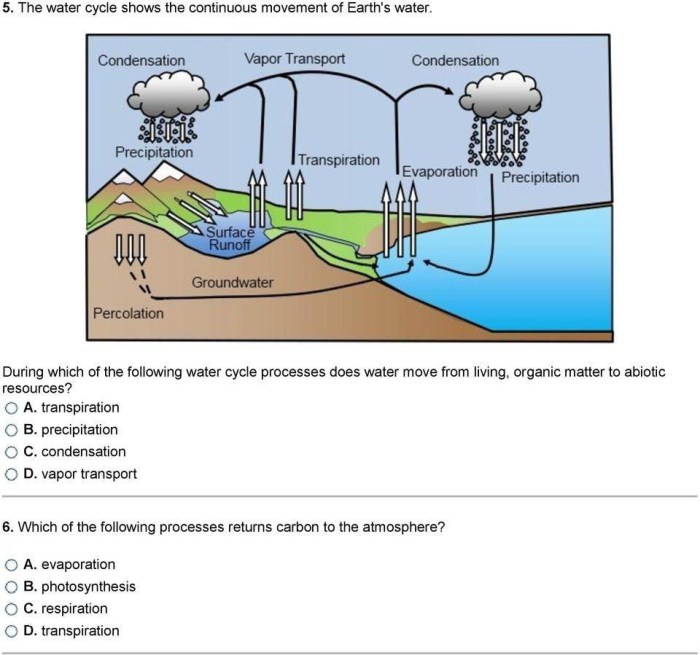
Water Cycle
The water cycle is the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. It is a complex system that involves water exchange between the atmosphere, land, and oceans. The sun’s energy drives the water cycle, causing water to evaporate from the Earth’s surface into the atmosphere.
The water vapor in the atmosphere then condenses into clouds, which eventually release the water back to the Earth as precipitation. Precipitation can take the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
Evaporation
Evaporation is the process by which water changes from a liquid to a gas. It occurs when water molecules absorb energy from their surroundings and move faster. As the water molecules move faster, they spread out and become less dense.
This causes them to rise into the atmosphere.
Condensation
Condensation is the process by which water vapor in the atmosphere changes back into a liquid. It occurs when water vapor molecules collide with cooler surfaces and lose energy. As the water vapor molecules lose energy, they slow down and come closer together.
This causes them to form water droplets.
Precipitation
Precipitation is the process by which water falls from the atmosphere to the Earth’s surface. It occurs when water droplets in clouds become too heavy to stay suspended in the air. Precipitation can take the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
Carbon Cycle

The carbon cycle is the continuous movement of carbon between the atmosphere, land, water, and living organisms. It is a complex system that involves carbon exchange between the atmosphere, land, oceans, and living organisms. The sun’s energy drives the carbon cycle, causing carbon to be released from the Earth’s surface into the atmosphere.
The carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is then absorbed by plants during photosynthesis. The plants use the carbon dioxide to produce food, which is then eaten by animals. The animals release the carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere when they breathe.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. It is a complex process that takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells. The glucose is used by the plants for energy, while the oxygen is released into the atmosphere.
Respiration
Respiration is the process by which animals use oxygen to convert glucose into carbon dioxide and water. It is a complex process that takes place in the mitochondria of animal cells. The carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere, while the water is used by the animals for various purposes.
Decomposition, Cycles of matter worksheet answers
Decomposition is the process by which dead plants and animals are broken down into simpler substances. It is a complex process that is carried out by bacteria and fungi. The bacteria and fungi release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, while the simpler substances are used by plants for growth.
Nitrogen Cycle
The nitrogen cycle is the continuous movement of nitrogen between the atmosphere, land, and water. It is a complex system that involves nitrogen exchange between the atmosphere, land, oceans, and living organisms. The sun’s energy drives the nitrogen cycle, causing nitrogen to be released from the Earth’s surface into the atmosphere.
The nitrogen gas in the atmosphere is then converted into ammonia by bacteria. The ammonia is then used by plants to produce proteins. The proteins are then eaten by animals. The animals release the nitrogen back into the atmosphere when they breathe.
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is the process by which nitrogen gas in the atmosphere is converted into ammonia. It is a complex process that is carried out by bacteria. The bacteria use the nitrogen gas to produce ammonia, which is then used by plants to produce proteins.
Nitrification
Nitrification is the process by which ammonia is converted into nitrate. It is a complex process that is carried out by bacteria. The bacteria use the ammonia to produce nitrate, which is then used by plants to produce proteins.
Denitrification
Denitrification is the process by which nitrate is converted back into nitrogen gas. It is a complex process that is carried out by bacteria. The bacteria use the nitrate to produce nitrogen gas, which is then released into the atmosphere.
Phosphorus Cycle
The phosphorus cycle is the continuous movement of phosphorus between the land, water, and living organisms. It is a complex system that involves phosphorus exchange between the land, oceans, and living organisms. The sun’s energy drives the phosphorus cycle, causing phosphorus to be released from the Earth’s surface into the water.
The phosphorus in the water is then absorbed by plants. The plants use the phosphorus to produce food, which is then eaten by animals. The animals release the phosphorus back into the water when they excrete waste.
Weathering
Weathering is the process by which rocks are broken down into smaller pieces. It is a complex process that is caused by the sun’s energy, wind, water, and ice. The weathering of rocks releases phosphorus into the water.
Plants
Plants absorb phosphorus from the water and use it to produce food. The food is then eaten by animals. The animals release the phosphorus back into the water when they excrete waste.
Animal Waste
Animal waste contains phosphorus. When the animal waste is deposited on the land, the phosphorus is released into the water. The phosphorus can then be absorbed by plants.
Sulfur Cycle: Cycles Of Matter Worksheet Answers

The sulfur cycle is the continuous movement of sulfur between the atmosphere, land, and water. It is a complex system that involves sulfur exchange between the atmosphere, land, oceans, and living organisms. The sun’s energy drives the sulfur cycle, causing sulfur to be released from the Earth’s surface into the atmosphere.
The sulfur dioxide in the atmosphere is then converted into sulfuric acid by bacteria. The sulfuric acid is then deposited on the land and in the water. The sulfur in the land and water is then used by plants to produce proteins.
The proteins are then eaten by animals. The animals release the sulfur back into the atmosphere when they breathe.
Volcanic Eruptions
Volcanic eruptions release sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere. The sulfur dioxide is then converted into sulfuric acid by bacteria. The sulfuric acid is then deposited on the land and in the water. The sulfur in the land and water is then used by plants to produce proteins.
Bacterial Decomposition
Bacteria decompose dead plants and animals. The decomposition process releases sulfur into the soil. The sulfur in the soil is then used by plants to produce proteins.
Oxidation
Oxidation is the process by which sulfur is converted into sulfuric acid. It is a complex process that is carried out by bacteria. The bacteria use the sulfur to produce sulfuric acid, which is then deposited on the land and in the water.
The sulfur in the land and water is then used by plants to produce proteins.
Q&A
What is the significance of the water cycle?
The water cycle is crucial for the distribution and availability of freshwater, supporting life and ecosystems across the globe.
How does photosynthesis contribute to the carbon cycle?
Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, converting it into organic matter, which plays a vital role in the cycling of carbon.
What is the role of denitrification in the nitrogen cycle?
Denitrification converts nitrates back into nitrogen gas, completing the nitrogen cycle and releasing nitrogen into the atmosphere.